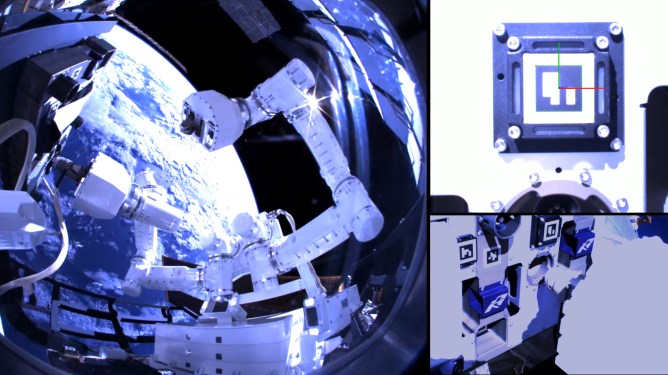
In a significant breakthrough, Los Angeles-based Gitai announced that its autonomous robotic arm has successfully completed a tech demonstration outside the International Space Station (ISS). This achievement is a crucial step towards reducing labor costs in space and paving the way for more complex tasks to be performed by robots.
Background: The Challenge of Labor Costs in Space
Human labor is expensive and dangerous in space. According to Gitai CEO Sho Nakanose, the company aims to reduce in-space labor costs by 100 times. This goal is achievable due to advancements in technology, particularly in robotics. Autonomous systems can perform tasks with precision and speed, making them an attractive alternative to human labor.
Gitai’s S2 Robotic Arm: A Key Player in Space Robotics
The 1.5-meter autonomous robotic arm, known as S2, was launched to the ISS aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 in January. The arm is mounted externally on Nanoracks’ Bishop Airlock and has successfully completed a series of tasks essential for building out structures to live and work in space. These tasks include:
- Installing a task panel: This involves securely fastening the panel to the airlock using robotic arms.
- Screwing and unscrewing tiny bolts: This requires precision and delicacy, making it an ideal task for robots.
- Manipulating flexible material: The arm must be able to handle various types of materials with care, ensuring that they are not damaged during transportation or installation.
- Attaching and detaching a flexible electric cable to a connector: This involves securely connecting the cable to the connector, which requires precision and attention to detail.
Gitai’s Vision for Space Robotics: On-Orbit Satellite Servicing
In addition to demonstrating its robotic arm’s capabilities, Gitai is also developing robotic satellites capable of performing tasks related to on-orbit satellite servicing. These tasks include:
- Rendezvous: The ability to dock with a satellite in space
- Docking: Securing the robotic satellite to the target satellite
- Inspection: Conducting thorough inspections of the satellite’s systems and components
- De-orbiting: Safely disposing of the satellite by re-entering the Earth’s atmosphere
Gitai plans to start offering on-orbit servicing in 2026, with its robotic arm technology readiness level (TRL) at an impressive 7, the highest level according to NASA.
Other Products and Future Plans
In addition to S2, Gitai is also developing an ‘inchworm-type’ arm, which has achieved a TRL of 7. This indicates that both products are highly advanced and ready for use in space applications.
Gitai’s Robotic Arms: A Leap Forward in Space Robotics
Gitai’s robotic arms represent a significant leap forward in space robotics, offering the potential to reduce labor costs and increase efficiency in space missions. With its focus on developing autonomous systems capable of performing complex tasks, Gitai is poised to make a major impact in the space industry.
Related Topics
- International Space Station: A habitable artificial satellite in low Earth orbit where humans live and work.
- Space Robotics: The use of robots in space exploration and development, particularly for tasks that require precision and delicacy.
- Autonomous Systems: Robots or machines capable of performing tasks independently without human intervention.